Sarcochilus
| Habit | orchid
| |
|---|---|---|
| Lifespan: | ⌛ | perennial |
| Features: | ✓ | flowers |
|---|
If this plant info box on watering; zones; height; etc. is mostly empty you can click on the edit tab and fill in the blanks!
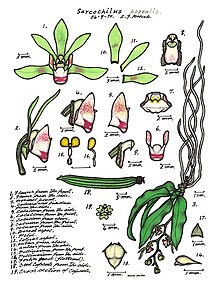

The genus Sarcochilus, abbreviated as Sarco in horticultural trade, is a member of the Orchid family (Orchidaceae), consisting of 25 species endemic to Northern Australia, Eastern Australia, Tasmania and New Caledonia.
The name Sarcochilus is derived from the Greek words sarx ( = flesh) and cheilos ( = lip), referring to the fleshy labellum of these orchids.
The genus Sarcochilus is shown to be non-monophyletic [1]
These are epiphytic or lithophytic orchids with leaves originating from a pseudobulb. The axillary, racemose inflorescence is pendant to arching with a few to many, successive opening flowers with free petals and sepals. The colour of the flowers is variable and goes from pure white (S. falcatus) to white and red (S. fitzgeraldii). The trilobed, fleshy labellum is saccate ( = pouch-like) and articulate to the apex of the column foot. The large side lobes are erect and curved. The small midlobe is attached to a short spur. Some of these species can form keikis, forming large clumps with age.
Many species have become endangered or vulnerable, due to illegal collecting.
Cultivation
Propagation
Pests and diseases
Species
- Sarcochilus aequalis D.L.Jones et M.A.Clem., 1991
- Sarcochilus australis (Lindl.) Rchb.f. in Walp., 1861 Butterfly Orchid
- Sarcochilus borealis (Nicholls) M.A.Clem.et D.L.Jones, 1989
- Sarcochilus ceciliae F.Muell., 1865 Fairy Bells (mostly a lithophyte)
- Sarcochilus chrysanthus Schltr., 1913
- Sarcochilus dilatatus F.Muell., 1859 Brown Butterfly Orchid (epiphyte)
- Sarcochilus falcatus R.Br., 1810 Orange Blossom Orchid (epiphyte)
- Sarcochilus fitzgeraldii F.Muell., 1870 Ravine Orchid (mainly lithophytic)
- Sarcochilus gildasii N.Hallé, 1986
- Sarcochilus hartmannii F.Muell., 1874 Hartmann's Orchid (almost completely lithophytic)
- Sarcochilus hillii (F.Muell.) F.Muell, 1860
- Sarcochilus hillii var. hillii.
- Sarcochilus hillii var. thycolus N.Hallé, 1986
- Sarcochilus hirticalcar (Dockrill) M.A.Clem. et B.J.Wallace, 1989
- Sarcochilus iboensis Schltr., 1913
- Sarcochilus koghiensis Schltr., 1911
- Sarcochilus odoratus Schltr., 1913
- Sarcochilus olivaceous Lindl., 1839
- Sarcochilus parviflorus Lindl. in Edwards’s, 1838
- Sarcochilus ramuanus (Kraenzl.) Schltr. in K.M.Schumann & C.A.G.Lauterbach, 1905
- Sarcochilus rarus Schltr., 1906
- Sarcochilus roseus (Clemesha) Clemesha, 1969 (true lithophyte)
- Sarcochilus serrulatus D.L.Jones, 1972
- Sarcochilus spathulatus R.S.Rogers, 1927
- Sarcochilus tricalliatus (Rupp) Rupp, 1951
- Sarcochilus uniflorus Schltr., 1913
- Sarcochilus weinthalii F.M.Bailey, 1903 Blotched Sarcophilus (epiphyte)
Hybrids
The species S. falcatus, S. fitzgeraldii and S. hartmannii have been hybridized, often with S. australis, producing rounder, cherry-red flowers. A few examples are : S.. Fitzhart (hartmannii x fitzgeraldii), S. Tin Yin Lara (Melody x fitzgeraldii), S. Southern Cross (hartmannii x australis) and S.. Otways Sunset (Fitzhart x australis).
Intrageneric hybrids include
- x Aeridochilus (Aerides x Sarcochilus)
- x Gastrosarcochilus (Gastrochilus x Sarcochilus)
- x Luichilus (Luisia x Sarcochilus)
- x Malcolmcampbellara (Drymoanthus x Plectorrhiza x Sarcochilus)
- x Parachilus (Parasarcochilus x Sarcochilus)
- x Plectochilus (Plectorrhiza x Sarcochilus)
- x Pomatochilus (Pomatocalpa x Sarcochilus)
- x Porterara (Rhynchostylis x Sarcochilus x Vanda)
- x Rhinochilus (Rhinerrhiza x Sarcochilus)
- x Sarcocentrum (Ascocentrum x Sarcochilus)
- x Sarcomoanthus (Sarcochilus x Drymoanthus)
- x Sarconopsis (Phalaenopsis x Sarcochilus)
- x Sarcorhiza (Rhinerrhiza x Sarcochilus)
- x Sarcothera (Renanthera x Sarcochilus)
- x Sarcovanda (Sarchilus x Vanda)
- x Sartylis (Rhynchostylis x Sarcochilus)
- x Sladeara (Doritis x Phalaenopsis x Sarcochilus)
- x Uptonara (Phalaenopsis x Rhynchostylis x Sarcochilus)
Gallery
References
- ↑ Topik Hidayat, Tomohisa Yukawa and Motomi Ito (August 2005). "Molecular phylogenetics of subtribe Aeridinae (Orchidaceae): insights from plastid matK and nuclear ribosomal ITS sequences". Journal of Plant Research 118 (4): 271–284. doi:10.1007/s10265-005-0217-3.
External links
- w:Sarcochilus. Some of the material on this page may be from Wikipedia, under the Creative Commons license.
- Sarcochilus QR Code (Size 50, 100, 200, 500)

